
 From St. Petersburg to Tianjin, Chasing a Dream
From St. Petersburg to Tianjin, Chasing a Dream Latin Expert Serves as Chinese Cultural Messenger
Latin Expert Serves as Chinese Cultural Messenger Bashan Site Complex: Unveiling Paleolithic Human Life
Bashan Site Complex: Unveiling Paleolithic Human Life Sci-Tech Week: Elevating Public Scientific Literacy
Sci-Tech Week: Elevating Public Scientific Literacy Can Solar Flares Harm Humans?
Can Solar Flares Harm Humans? China's Medium-voltage Micro-grid Technology Making Overseas Debut
China's Medium-voltage Micro-grid Technology Making Overseas Debut
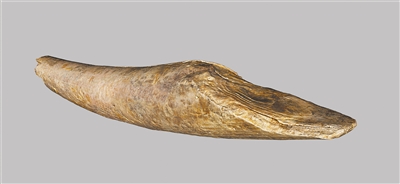 |
| An ivory shovel unearthed from the Bashan site complex. (PHOTO: XINHUA) |
The Bashan site complex, a cluster of over 80 Paleolithic Age sites, is located around Bashan in Yishui county, Shandong province in east China. It was listed as one of China's top 10 archaeological discoveries in 2023.
The discovery not only established a comprehensive archaeological cultural sequence in the upper reaches of the Yihe River from 100,000 years to 10,000 years ago, but also unveiled a vivid picture of ancient human life.
The Bashan site complex was discovered by accident. In July 2020, during flood discharges from the Bashan reservoir along the main stream of the Yihe, an ivory artifact was washed ashore, leading to exploration and excavation.
After three years of excavation, over 40,000 relics were unearthed from a 225 square meter area. They included 30,000 stone artifacts, over 10,000 animal bones, and a small number of organic specimens such as bamboo and wood.
Particularly noteworthy is an ivory shovel unearthed from the site. Dating tests indicate it was made not later than 99,000 years ago. The ivory came from an adult straight-tusked elephant that weighed 10 to 15 tons, lived in the late Pleistocene era between 10,000 and 200,000 years ago, and was the largest elephant species in history.
Some animal fossils unearthed from the Bashan site have revealed, for the first time, the full utilization of giant animal resources by humans 100,000 years ago, demonstrating their adaptation strategies and historical scenes in the face of environmental changes in the Huang-Huai-Hai region.






